Xenopeltis unicolor
| Xenopeltis unicolor | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Vertebrata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Xenopeltidae |
| Genus: | Xenopeltis |
| Species: | X. unicolor |
| Binomial name | |
| Xenopeltis unicolor Reinwardt, 1827 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
- Common names: sunbeam snake.[2]
Xenopeltis unicolor is a non-venomous sunbeam snake species found in Southeast Asia and some regions of Indonesia. This is a primitive snake known for both its highly iridescent scales and its ability to reproduce quickly, as it is oviparous and as such can lay up to 10 eggs at a time. No subspecies are currently recognized.[3]
Description
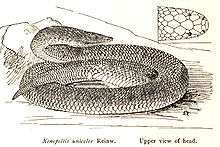
Grows to an average of about 1 m (3 ft 3 in). A fossorial species, the head is wedge-shaped and narrow with little neck delineation, which makes it easy to push through the soil. Its most defining characteristic is its iridescent, highly polished scales that give this snake its common name. They have a layer of dark pigmentation just below the surface on each scale that enhances the iridescence. The youngs look very similar to the adults, except that they have a strong white "collar" of scales evident just below the head. This coloration fades within the first year.
This is a primitive form of snake with both boid and python characteristics; which family it belongs to is still a matter of debate.
Geographic range
Found in China (Guangdong and Yunnan), Myanmar, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, West Malaysia, Penang Island, Singapore Island, East Malaysia (Sarawak), Indonesia (the Riau Archipelago, Bangka, Billiton, Sumatra, We, Simalur, Nias, the Mentawai Islands [Siberut], Borneo, Java and Sulawesi) and the Philippines (Balabac, Bongao, Jolo and Palawan). The type locality given is "Java".[1]
Habitat
Tends to live in open areas such as forest clearings, gardens and parks. Often encountered in rice paddies.
Behavior
These snake are constrictors, killing their prey by suffocation in their muscular coils. They are fossorial and spend most of their time below ground. They may bite readily if handled roughly, but mostly just try to escape if picked up. They are also observed to vibrate their tails in a rattlesnake-like fashion when they feel threatened.
Feeding
The diet is varied, consisting primarily of frogs, reptiles, including other snakes, and small mammals.
Reproduction
Oviparous, with females laying up to 10 eggs at a time.
See also
- Xenopeltidae by common name
- Xenopeltidae by taxonomic synonyms
References
- 1 2 McDiarmid RW, Campbell JA, Touré T. 1999. Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, Volume 1. Washington, District of Columbia: Herpetologists' League. 511 pp. ISBN 1-893777-00-6 (series). ISBN 1-893777-01-4 (volume).
- ↑ Mehrtens JM. 1987. Living Snakes of the World in Color. New York: Sterling Publishers. 480 pp. ISBN 0-8069-6460-X.
- ↑ "Xenopeltis unicolor ". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 1 September 2007.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Xenopeltis unicolor. |
- Xenopeltis unicolor at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 1 September 2007.
- Sunbeam Snake at Ecology Asia. Accessed 18 September 2008.
- Photos and videos of Xenopeltis unicolor