Zileuton
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Zyflo |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697013 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Not yet established |
| Protein binding | 93% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP1A2, CYP2C9 and CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Biological half-life | 2.5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
111406-87-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 60490 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 5297 |
| DrugBank |
DB00744 |
| ChemSpider |
54531 |
| UNII |
V1L22WVE2S |
| KEGG |
D00414 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:10112 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL93 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.121.111 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H12N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 236.291 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Zileuton (trade name ZYFLO) is an orally active inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase, and thus inhibits leukotrienes (LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4) formation. Zileuton is used for the maintenance treatment of asthma. Zileuton was introduced in 1996 by Abbott Laboratories and is now marketed in two formulations by Cornerstone Therapeutics Inc. under the brand names ZYFLO and ZYFLO CR. The original immediate-release formulation of zileuton, known as ZYFLO, is taken four times per day. The extended-release formulation, ZYFLO CR, is taken twice daily.
Although the 600 mg immediate release tablet (Zyflo) and extended release formulation of zileuton is still available (Zyflo CR), the 300 mg immediate release tablet was withdrawn from the U.S. market on February 12, 2008.[1][2]
Pharmacotherapy
Indications and dosing
Zileuton is indicated for the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma in adults and children 12 years of age and older. Zileuton is not indicated for use in the reversal of bronchospasm in acute asthma attacks. Therapy with zileuton can be continued during acute exacerbations of asthma.
The recommended dose of ZYFLO is one 600 mg tablet, four times per day. The tablets may be split in half to make them easier to swallow. The recommended dose of ZYFLO CR is two 600 mg extended-release tablets twice daily, within one hour after morning and evening meals, for a daily dose of 2400 mg. Do not split ZYFLO CR tablets in half.
Related compounds include montelukast (Singulair) and zafirlukast (Accolate). These two compounds are leukotriene receptor antagonists which block the action of specific leukotrienes, while zileuton inhibits leukotriene formation.
Research on mice suggests that Zileuton used alone or in combination with imatinib may inhibit chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).[3]
Contraindications and warnings
The most serious side effect of ZYFLO and ZYFLO CR is a potential elevation of liver enzymes (in 2% of patients). Therefore, zileuton is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease or persistent hepatic function enzymes elevations greater than three times the upper limit of normal. Hepatic function should be assessed prior to initiating ZYFLO CR, monthly for the first 3 months, every 2–3 months for the remainder of the first year, and periodically thereafter.
Neuropsychiatric events, including sleep disorders and behavioral changes, may occur with ZYFLO and ZYFLO CR. Patients should be instructed to notify their healthcare provider if neuropsychiatric events occur while using ZYFLO or ZYFLO CR.
Zileuton is a weak inhibitor of CYP1A2[4] and thus has three clinically important drug interactions, which include increasing theophylline, and propranolol levels. It has been shown to lower theophylline clearance significantly, doubling the AUC and prolonging half-life by nearly 25%. Because of theophylline's relation to caffeine (both being a methylxanthine, and theophylline being a metabolite of caffeine), caffeine's metabolism and clearance may also be reduced, but there are no drug interaction studies between zileuton and caffeine.[5] The R-isomer of warfarin metabolism and clearance is mainly affected by zileuton, while the S-isomer is not (because of metabolism via different enzymes). This can lead to an increase in prothrombin time.[6]
Chemistry
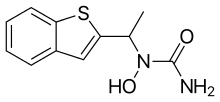
Zileuton is an active oral inhibitor of the enzyme 5-lipoxygenase, which forms leukotrienes, 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, and 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid from arachidonic acid. The chemical name of zileuton is (±)-1-(1-Benzo[b]thien-2-ylethyl)-l-hydroxyurea.[7]
The molecular formula of zileuton is C11H12N2O2S with a molecular weight of 236.29. The formulation from the manufacturer is a racemic mixture of R(+) and S(-) enantiomers.[8]
Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration zileuton is rapidly absorbed with a mean time to peak blood serum concentration of 1.7 hours and an average half-life elimination of 2.5 hours. Blood plasma concentrations are proportional to dose, whereas the absolute bioavailability is unknown.
The apparent volume of distribution of zileuton is approximately 1.2 L/kg. Zileuton is 93% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to albumin, with minor binding to alpha-1-acid glycoprotein.
Elimination of zileuton is primarily through metabolites in the urine (~95%) with the feces accounting for the next largest amount (~2%). The drug is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzymes: CYP1A2, 2C9, and 3A4.[8]
Adverse effects
The most common adverse reactions reported by patients treated with ZYFLO CR were sinusitis (6.5%), nausea (5%), and pharyngolaryngeal pain (5%) vs. placebo, 4%, 1.5%, and 4% respectively.
Interactions
Drug interactions
Zileuton is a minor substrate of CYP1A2, 2C8/9, 3A4, and a weak inhibitor of CYP 1A2. The drug has been shown to increase the serum concentration or effects of theophylline, propranolol, and warfarin, although significant increase in prothrombin time is not obvious. It is advised that the doses of each medication be monitored and/or reduced accordingly.
Other interactions
The avoidance of alcohol is recommended due to increase risk of CNS depression as well as an increase risk in liver toxicity. In addition, the herbal supplement St. John's wort may decrease the serum levels of zileuton.[9]
Overdose/toxicology
Symptoms
Human experience of acute overdose with zileuton is limited. A patient in a clinical study took between 6.6 and 9.0 grams of zileuton immediate-release tablets in a single dose. Vomiting was inducted and the patient recovered without sequelae. Zileuton is not removed by dialysis.
The oral minimum lethal doses in mice and rats were 500-4000 and 300–1000 mg/kg, respectively (providing greater than 3 and 9 times the systemic exposure (AUC) achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose, respectively). In dogs, at an oral dose of 1000 mg/kg (providing in excess of 12 times the systemic exposure (AUC) achieved at the maximum recommended human daily oral dose) no deaths occurred by nephritis was reported.
Treatment
Should an overdose occur, the patient should be treated symptomatically and supportive measures instituted as required. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed drug should be achieved by emesis or gastric lavage; usual precautions should be observed to maintain the airway. A Certified Poison Control Center should be consulted for up-to-date information on management of overdose with ZYFLO CR.
See also
References
- ↑ Zileuton (Oral Route) - MayoClinic
- ↑ Zyflo consumer information - Drugs.com
- ↑ ScienceDaily (June 8, 2009),Lethal Cancer Knocked Down By One-two Drug Punch
- ↑ Lu P, Schrag ML, Slaughter DE, Raab CE, Shou M, Rodrigues AD (November 2003). "Mechanism-based inhibition of human liver microsomal cytochrome P450 1A2 by zileuton, a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 31 (11): 1352–60. doi:10.1124/dmd.31.11.1352. PMID 14570767.
- ↑ Cafcit (caffeine citrate) package insert. Evansville, IN: Mead Johnson & Company; 2003 May.
- ↑ Zyflo Filmtab (zileuton) package insert. Chicago, IL: Abbott Laboratories; 1998 Mar.
- ↑ Krutetskaya, Z. I.; Milenina, L. S.; Naumova, A. A.; Antonov, V. G.; Nozdrachev, A. D. (2016). "5-Lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton inhibits Ca2+-responses induced by glutoxim and molixan in macrophages". Doklady Biochemistry and Biophysics. 469 (1): 302–304. doi:10.1134/S1607672916040177. ISSN 1607-6729.
- 1 2 Zyflo Drug Information
- ↑ Zileuton monograph. Lexi-Comp Online, Lexi-Drugs Online, Lexi-Comp Inc. Hudson, OH. Available at: "Archived copy". Archived from the original on November 16, 2004. Retrieved September 14, 2008.. Accessed November 12th, 2008.