Deimos (moon)
|
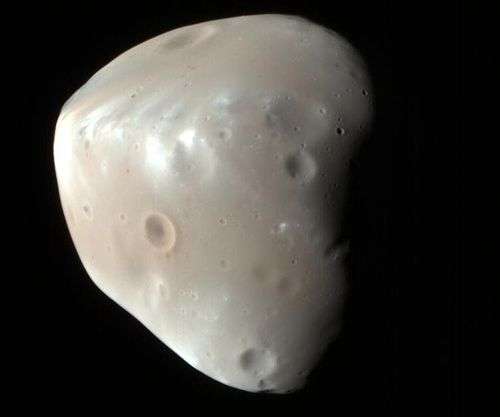
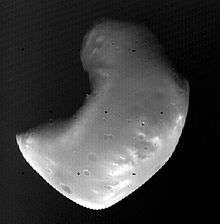
An enhanced-color image of Deimos (MRO, 21 February 2009). Image: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Asaph Hall |
| Discovery date | 12 August 1877 |
| Designations | |
| Adjectives | Deimosian |
| Orbital characteristics | |
|
Epoch 2012-Sep-21 (JD 2456191.5) | |
| Periapsis | 23455.5 km |
| Apoapsis | 23470.9 km |
| 23463.2 km[1] (6.92 Mars radii) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.00033[1] |
|
1.263 d[1] (30.312 h) | |
Average orbital speed | 1.3513 km/s[2] |
| Inclination |
0.93° (to Mars's equator) 1.791° (to the local Laplace plane)[1] 27.58° (to the ecliptic) |
| Satellite of | Mars |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 15 × 12.2 × 11 km[3] |
Mean radius |
6.2 ± 0.18 km[4] (0.97316 mEarths) |
|
495.1548 km2 (97.0755 µEarths) | |
| Volume |
999.78 km3 (92.2979 nEarths) |
| Mass |
1.4762×1015 kg[2] (0.247179 nEarths) |
Mean density | 1.471±0.166 g/cm3[4] |
|
0.003 m/s2[2] (306 µg) | |
|
5.556 m/s (20 km/h)[2] | |
| Synchronous[1] | |
| Albedo | 0.068 ± 0.007[4] |
| Temperature | ≈ 233 K |
|
| |
Deimos (systematic designation: Mars II)[5] is the smaller and outer of the two natural satellites of the planet Mars, the other being Phobos. Deimos has a mean radius of 6.2 km (3.9 mi)[1] and takes 30.3 hours[1] to orbit Mars. The name Deimos is pronounced /ˈdaɪmɒs/ DY-mos, or sometimes /ˈdiːməs/ DEE-məs or like the Greek Δεῖμος. In Greek mythology, Deimos was the twin brother of Phobos and personified terror.
Deimos is 23,460 km (14,580 mi) from Mars, much further than Mars's other moon, Phobos.[6]
Discovery
Deimos was discovered by Asaph Hall, Sr. at the United States Naval Observatory in Washington, D.C on 12 August 1877, at about 07:48 UTC (given in contemporary sources as "11 August 14:40" Washington mean time, using an astronomical convention of beginning a day at noon, so 12 hours must be added to get the actual local mean time).[8][9][10][11] Hall also discovered Phobos on 18 August 1877, at about 09:14 GMT, after deliberately searching for Martian moons.
It is named after Deimos, a figure representing dread in Greek Mythology.[5] The names, at first spelled Phobus and Deimus, were suggested by Henry Madan (1838–1901),[5] Science Master of Eton, from Book XV of the Iliad, where Ares (the Roman god Mars) summons Dread (Deimos) and Fear (Phobos).[12]
Physical characteristics
Deimos, like Mars's other moon, Phobos, has spectra, albedos and densities similar to those of a C- or D-type asteroid. Like most bodies of its size, Deimos is highly non-spherical with triaxial dimensions of 15 × 12.2 × 11 km,[3] making it 0.56 times the size of Phobos. Deimos is composed of rock rich in carbonaceous material, much like C-type asteroids and carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. It is cratered, but the surface is noticeably smoother than that of Phobos, caused by the partial filling of craters with regolith. The regolith is highly porous and has a radar-estimated density of only 1.471 g/cm3.[14]
It has an escape velocity of 5.6 m/s[2] and an apparent magnitude of 12.45.[4]
Named geological features
Only two geological features on Deimos have been given names. The craters Swift and Voltaire are named after writers who speculated on the existence of two Martian moons before Phobos and Deimos were discovered.[15]
| Crater | Named after | Coordinates | Diameter (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swift | Jonathan Swift | 12°30′N 358°12′W / 12.5°N 358.2°W | 1000 |
| Voltaire | Voltaire | 22°00′N 3°30′W / 22°N 3.5°W | 1900[17] |
Orbital characteristics

Deimos's orbit is nearly circular and is close to Mars's equatorial plane. Deimos is possibly an asteroid that was perturbed by Jupiter into an orbit that allowed it to be captured by Mars, though this hypothesis is still controversial and disputed.[18] Both Deimos and Phobos have very circular orbits which lie almost exactly in Mars's equatorial plane, and hence a capture origin requires a mechanism for circularizing the initially highly eccentric orbit, and adjusting its inclination into the equatorial plane, most likely by a combination of atmospheric drag and tidal forces,[19] although it is not clear that sufficient time was available for this to have occurred for Deimos.[18]

As seen from Mars, Deimos would have an angular diameter of no more than 2.5 minutes (sixty minutes make one degree), one twelfth of the width of the Moon as seen from Earth, and would therefore appear almost star-like to the naked eye.[20] At its brightest ("full moon") it would be about as bright as Venus is from Earth; at the first- or third-quarter phase it would be about as bright as Vega. With a small telescope, a Martian observer could see Deimos's phases, which take 1.2648 days (Deimos's synodic period) to run their course.[20]
Unlike Phobos, which orbits so fast that it actually rises in the west and sets in the east, Deimos rises in the east and sets in the west. However, the Sun-synodic orbital period of Deimos of about 30.4 hours exceeds the Martian solar day ("sol") of about 24.7 hours by such a small amount that 2.7 days elapse between its rising and setting for an equatorial observer.
Because Deimos's orbit is relatively close to Mars and has only a very small inclination to Mars's equator, it cannot be seen from Martian latitudes greater than 82.7°.
Solar transits

Deimos regularly passes in front of the Sun as seen from Mars. It is too small to cause a total eclipse, appearing only as a small black dot moving across the Sun. Its angular diameter is only about 2.5 times the angular diameter of Venus during a transit of Venus from Earth. On 4 March 2004 a transit of Deimos was photographed by Mars Rover Opportunity, and on 13 March 2004 a transit was photographed by Mars Rover Spirit.
Origin
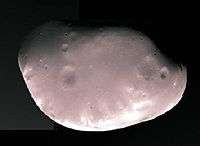
The origin of Mars's moons is unknown and the hypotheses are controversial.[18] The main hypotheses are that they formed either by capture or by accretion. Because of the similarity to the composition of C- or D-type asteroids, one hypothesis is that the moons may be objects captured into Martian orbit from the asteroid belt, with orbits that have been circularized either by atmospheric drag or tidal forces,[21] as capture requires dissipation of energy. The current Martian atmosphere is too thin to capture a Phobos-sized object by atmospheric braking.[18] Geoffrey Landis has pointed out that the capture could have occurred if the original body was a binary asteroid that separated due to tidal forces.[22] The main alternative hypothesis is that the moons accreted in the present position. Another hypothesis is that Mars was once surrounded by many Phobos- and Deimos-sized bodies, perhaps ejected into orbit around it by a collision with a planetesimal.[23][24]
Exploration

Overall, its exploration history is similar to those of Mars and of Phobos.[25] Deimos has been photographed in close-up by several spacecraft whose primary mission has been to photograph Mars. No landings on Deimos have been made.
The Soviet Phobos program sent two probes to Phobos. In case Phobos 1 succeeded, Phobos 2 could have been sent to Deimos. Both probes launched successfully in July 1988. The first was lost en route to Mars, whereas the second returned some data and images but failed shortly before beginning its detailed examination of Phobos's surface, including a lander.
In 1997 and 1998, the proposed Aladdin mission was selected as a finalist in the NASA Discovery Program. The plan was to visit both Phobos and Deimos, and launch projectiles at the satellites. The probe would collect the ejecta as it performed a slow flyby (~1 km/s).[26] These samples would be returned to Earth for study three years later.[27][28] The principal investigator was Carle Pieters of Brown University. The total mission cost, including launch vehicle and operations was $247.7 million.[29] Ultimately, the mission chosen to fly was MESSENGER, a probe to the planet Mercury.[30]
In 2008, NASA Glenn Research Center began studying a Phobos and Deimos sample return mission that would use solar electric propulsion. The study gave rise to the "Hall" mission concept, a New Frontiers-class mission currently under further study.[31]
Also, the sample return mission called Gulliver has been conceptualized and dedicated to Deimos,[32] in which 1 kilogram (2.2 pounds) of material from Deimos would be returned to Earth.[32]
Another concept of sample-return mission from Phobos and Deimos is OSIRIS-REx 2, which would use heritage from the first OSIRIS-REx.[33]
In March 2014, a Discovery class mission was proposed to place an orbiter on Mars orbit by 2021 and study Phobos and Deimos. It is called Phobos And Deimos & Mars Environment (PADME).[34][35]
In fiction
- Id Software's 1993 game Doom has its second episode set on Deimos.
- Bungie's 1994 game Marathon takes place on Deimos which was converted into a deep space colony spaceship.
- In Green Mars by Kim Stanley Robinson, Deimos is ejected into space from orbit as a preventative measure against it being used as a weapons platform to bomb the surface of Mars as Phobos had been.
- Deimos is the location of an alien weapon in the 2010 novel Impact by Douglas Preston.
- Tezuka Productions's anime TV series Astro Boy (2003 TV series) has its fifth episode set on Deimos.
See also
- List of missions to the moons of Mars
- List of natural satellites
- Moons of Mars
- Phobos and Deimos in fiction
- Transit of Deimos from Mars
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "HORIZONS Web-Interface". NASA. 21 September 2013. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Mars: Moons: Deimos". NASA Solar System Exploration. 30 September 2003. Retrieved 2 December 2013.
- 1 2 "Deimos". Retrieved June 6, 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 "Planetary Satellite Physical Parameters". Jet Propulsion Laboratory (Solar System Dynamics). 13 July 2006. Retrieved 29 January 2008.
- 1 2 3 Blunck, Jürgen (2009). "The Satellites of Mars; Discovering and Naming the Satellites". Solar System Moons: Discovery and Mythology. Springer. p. 5. ISBN 978-3-540-68852-5.
- ↑ Staff (2016). "Deimos". SeaSky.org. Retrieved 23 January 2016.
- ↑ "Deimos – Viking 2 Orbiter". NASA NSSDC. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ↑ Hall, A.; Observations of the Satellites of Mars, Astronomische Nachrichten, Vol. 91, No. 2161 (17 October 1877, signed 21 September 1877) pp. 11/12–13/14
- ↑ Morley, T. A.; A Catalogue of Ground-Based Astrometric Observations of the Martian Satellites, 1877–1982, Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, Vol. 77, No. 2 (February 1989), pp. 209–226 (Table II, p. 220: first observation of Deimos on 1877-08-12.32526)
- ↑ Notes: The Satellites of Mars, The Observatory, Vol. 1, No. 6 (20 September 1877), pp. 181–185
- ↑ The Discovery of the Satellites of Mars, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 38, No. 4, (8 February 1878), pp. 205–209
- ↑ Hall, A.; Names of the Satellites of Mars, Astronomische Nachrichten, Vol. 92, No. 2187 (14 March 1878, signed 7 February 1878), p. 47/48
- ↑ Deimos - Viking 2 Orbiter
- ↑ Busch, M. W.; et al. (2007). "Arecibo Radar Observations of Phobos and Deimos". Icarus. 186 (2): 581–584. Bibcode:2007Icar..186..581B. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2006.11.003.
- ↑ of Planetary Nomenclature, USGS Astrogeology Research Program
- ↑ Lakdawalla, Emily (9 March 2009). "Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter eye candy: HiRISE images Deimos". Planetary Society. Retrieved 19 August 2013.
- ↑ Nomenclature: Crater, craters
- 1 2 3 4 Burns, J. A., "Contradictory Clues as to the Origin of the Martian Moons," in Mars, H. H. Kieffer et al., eds., U. Arizona Press, Tucson, 1992
- 1 2 Richardson, R. S., If You Were on Mars, Astronomical Society of the Pacific Leaflets, Vol. 4, Leaflet No. 178 (December 1943), pp. 214–221
- ↑ Landis, G. A., "Origin of Martian Moons from Binary Asteroid Dissociation," American Association for the Advancement of Science Annual Meeting; Boston, MA, 2001; abstract.
- ↑ Craddock, R. A.; (1994); The Origin of Phobos and Deimos, Abstracts of the 25th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, held in Houston, TX, 14–18 March 1994, p. 293
- ↑ "Close Inspection for Phobos".
accumulated ejecta from asteroid impacts on the Martian surface
- ↑ Mars Phobos and Deimos Survey (M-PADS)–A Martian Moons Orbiter and Phobos Lander (Ball, Andrew J.; Price, Michael E.; Walker, Roger J.; Dando, Glyn C.; Wells, Nigel S. and Zarnecki, John C. (2009). Mars Phobos and Deimos Survey (M-PADS)–A Martian Moons Orbiter and Phobos Lander. Advances in Space Research, 43(1), pp. 120–127.)
- ↑ Barnouin-Jha, Olivier S. "Aladdin: sample return from the moons of Mars". Aerospace Conference, 1999. Proceedings. 1999 IEEE. Aerospace Conference, 1999. Proceedings. 1999 IEEE. Retrieved 28 March 2013.
- ↑ Pieters, Carle. "ALADDIN: PHOBOS -DEIMOS SAMPLE RETURN" (PDF). 28th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference. 28th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference. Retrieved 28 March 2013.
- ↑ "Messenger and Aladdin Missions Selected as NASA Discovery Program Candidates". Retrieved 28 March 2013.
- ↑ "Five Discovery mission proposals selected for feasiblilty studies". Retrieved 28 March 2013.
- ↑ "NASA Selects Missions to Mercury and a Comet's Interior as Next Discovery Flights". Retrieved 28 March 2013.
- ↑ Lee, P. et al. 2010. Hall: A Phobos and Deimos Sample Return Mission. 44th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., The Woodlands, TX. 1–5 Mar 2010. [#1633] Bibcode: 2010LPI....41.1633L.
- 1 2 Dr. Britt - The Gulliver Mission: Sample Return from Deimos
- ↑ Elifritz, T. L. - OSIRIS-REx II to Mars
- ↑ Lee, Pascal; Bicay, Michael; Colapre, Anthony; Elphic, Richard (March 17–21, 2014). Phobos And Deimos & Mars Environment (PADME): A LADEE-Derived Mission to Explore Mars's Moons and the Martian Orbital Environment. (PDF). 45th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2014).
- ↑ Reyes, Tim (1 October 2014). "Making the Case for a Mission to the Martian Moon Phobos". Universe Today. Retrieved 2014-10-05.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Deimos (moon). |
- Deimos Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- Deimos rotation movie
- Animation of Deimos
- USGS Deimos nomenclature