Emerald Necklace
| Emerald Necklace | |
|---|---|
|
Boston Public Garden, the second "jewel" of the Emerald Necklace | |
| Type | Public park |
| Location | Boston and Brookline, Massachusetts, United States |
| Created | 1860s |
| Operated by | Emerald Necklace Conservancy |
| Open |
All year |
|
Olmsted Park System | |
 | |
   | |
| Location | Boston and Brookline, Massachusetts |
| Coordinates | 42°19′34″N 71°06′52″W / 42.32611°N 71.11444°WCoordinates: 42°19′34″N 71°06′52″W / 42.32611°N 71.11444°W |
| Built | 1870 |
| Architect | Olmsted, Frederick Law, Sr. |
| NRHP Reference # | [1] |
| Added to NRHP | December 8, 1971 |
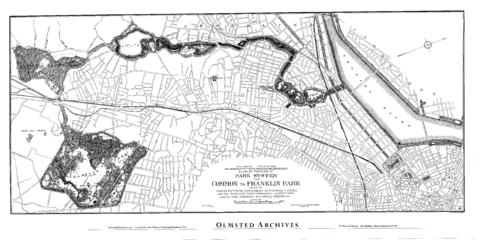
The Emerald Necklace consists of a 1,100-acre (4.5 km2), or 445-hectare chain of parks linked by parkways and waterways in Boston and Brookline, Massachusetts. It gets its name from the way the planned chain appears to hang from the "neck" of the Boston peninsula; to this day it is not fully constructed. In 1989 the Emerald Necklace Parks was designated as Boston Landmark by the Boston Landmarks Commission.
Overview
The Necklace comprises half of the City of Boston's park acreage, parkland in the Town of Brookline, and parkways and park edges under the jurisdiction of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. More than 300,000 people live within its watershed area. From Boston Common to Franklin Park it is approximately seven miles by foot or bicycle through the parks.[2]
The Emerald Necklace includes:
- Boston Common
- Public Garden
- Commonwealth Avenue Mall
- The Fens
- The Riverway
- Olmsted Park
- Jamaica Pond
- Jamaicaway
- Arborway
- Arnold Arboretum
- Franklin Park
Several components of the Emerald Necklace pre-date the plan to unite them. Some links of the Emerald Necklace not only offer an opportunity for recreation in a wooded environment, but are also ecologically important urban wilds that provide nesting places for migratory birds and improve the air quality of the city.
History


This linear system of parks was designed by Frederick Law Olmsted to connect Boston Common, dating from the colonial period, and Public Garden (1837) to Franklin Park, known as the "great country park."
The project began around 1878 with the effort to clean up and control the marshy area which became the Back Bay and The Fens. In 1880, Olmsted proposed that the Muddy River, which flowed from Jamaica Pond through the Fens, be included in the park plan. The current was dredged into a winding stream and directed into the Charles River. The corridor encompassing the river became the linear park still in existence today. Olmsted's vision of a linear park of walking paths along a gentle stream connecting numerous small ponds was complete by the turn of the century. The parks conceived by Olmsted, from Storrow Drive south to Franklin Park, were collectively listed on the National Register of Historic Places as the Olmsted Park System.[3]
Over the past decade, almost $60 million in capital expenditures for parks and waterway improvements have been made in the Emerald Necklace by the City of Boston and the Town of Brookline. These efforts have included improved pathways, plantings and signage, bridge repairs, and the restoration of boardwalks and buildings. In some areas (especially the woodlands of Franklin Park and Olmsted Park) these efforts have only begun to address the over 50 years of neglect the Emerald Necklace has suffered.[2]
Several dedicated parks organizations, including the Emerald Necklace Conservancy, the Friends of the Public Garden, the Franklin Park Coalition, and the Arboretum Park Conservancy, were created to protect, maintain, restore and advocate for the Emerald Necklace parks through the work of their staff, the donations of their constituents and the efforts of their volunteers.[4]
Shape
The Emerald Necklace begins near Boston's Downtown Crossing, proceeds along the Boston/Brookline border, then curves into Jamaica Plain. At the south border of Arnold Arboretum, at the point most distant from its beginning, the Emerald Necklace is in Roslindale. It then hooks back up into Roxbury and Dorchester.
Olmsted's original plan called for a "U" shaped necklace which terminated at Boston Harbor. The final link, the Dorchesterway, was never realized.[5]Jurisdiction
- Arnold Arboretum is leased to and managed by Harvard University.
- The west banks of Olmsted Park and the Riverway are under the jurisdiction of Brookline Parks & Open Space.
- The majority of the Emerald Necklace is maintained by Boston Parks and Recreation with a small portion belonging to the Department of Conservation and Recreation.[6]
The Emerald Necklace Conservancy
The Emerald Necklace Conservancy was created to protect, restore, maintain and promote the landscape, waterways and parkways of the Emerald Necklace park system as special places for people to visit and enjoy.
The Conservancy's programs and funding support and complement initiatives by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, City of Boston and Town of Brookline who began the Necklace's restoration in the 1980s.
A public-private partnership, the Conservancy was formed in 1996 and incorporated in 1998 as a non-profit organization. The organization brings together government, business, residential and institutional representatives, community leaders and organizations, and environmental and park advocates in support of the Olmsted legacy. President Julie Crockford and the staff work closely with the Board of Directors, the Park Overseers (representing all of the parks and friends groups within the Emerald Necklace), the Stewardship Council, and hundreds of volunteers to accomplish their mission.
Plans
The Emerald Necklace Parks Master Plan was completed in 1989, and updated in 2001.[7]
The parks have long been subject to flooding from the Muddy River. The Muddy River Restoration Project[8] will dredge contaminated sediments and implement other major structural improvements, unburying the river and improving its integrity, appearance, and flood control capabilities. Phase I - Daylighting the river at the Landmark Center began spring 2009.[9]
See also
- Charles River Esplanade
- Columbia Road
- Forest Hills Cemetery
- Larz Anderson Park
- Massachusetts Audubon Society
- National Register of Historic Places listings in:
- Southwest Corridor Park
- Rose Kennedy Greenway
References
- ↑ National Park Service (2007-01-23). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- 1 2 "City of Boston - The Emerald Necklace".
- ↑ "NRHP nomination for Olmsted Park System". Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Retrieved 2014-05-20.
- ↑ "The Emerald Necklace Conservancy - Welcome!". Emeraldnecklace.org. Retrieved 2012-05-20.
- ↑ "Heart of the City Project, Center for Urban and Regional Policy, Harvard University and Northeastern University".
- ↑ "Parks & Recreation | City of Boston". Cityofboston.gov. 2012-01-18. Retrieved 2012-05-20.
- ↑ "Olmsted's Emerald Necklace". Muddyrivermmoc.org. Retrieved 2012-05-20.
- ↑ "Welcome to the MMOC". Muddyrivermmoc.org. 2012-04-11. Retrieved 2012-05-20.
- ↑ "Muddy River Restoration Project". Muddyrivermmoc.org. Retrieved 2012-05-20.
External links
- The Emerald Necklace Conservancy
- City of Boston Website
- Friends of the Public Garden
- A complete 1894 plan