Prehistoric Europe

Prehistoric Europe refers to the prehistorical period of Europe, usually taken to refer to human prehistory since the Lower Paleolithic, but in principle also extending to the geological time scale – for which see Geological history of Europe.
From the Lower Paleolithic, approximately 1.8 million[1] years ago, until 40,000 years ago,[2] Europe was populated by Homo erectus and Homo neanderthalensis. In the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic, from about 43,000[3] to 6,000 years ago, Europe had Homo sapiens hunter-gatherer populations.[4] During the last glacial maximum, much of Europe was depopulated and re-settled, about 15,000 years ago. The European Neolithic began about 9,000 years ago in southeastern Europe, and reached northern Europe by about 5,000 years ago.
The forerunner to the Bronze age was the Chalcolithic or Copper age; an archaeological site in Serbia contains the worlds oldest securely dated evidence of copper making at high temperature, from 7,500 years ago.[5]
The European Bronze Age begins from about 3200 BC in Greece. The European Iron Age begins from about 1200 BC, spreading to northern Europe by 500 BC. During the Iron Age, Europe gradually enters the historical period. Literacy came to the Mediterranean world from as early as the 8th century BC (Classical Antiquity), but northern Europe, including northern Russia, remained in the prehistoric period until as late as the Middle Ages, around AD 1200. Around that date, Swedish and German expansion in the Northern Crusades brought the lands of the eastern Baltic into the historical record, while present-day northern Russia entered the historical record as a result of Russian expansion northward under the Novgorod Republic. Thus, much of Europe was in a stage of proto-history for a long period.
Stone Age
Paleolithic
Lower Paleolithic
The earliest inhabitants of Europe from 1.8 million years ago used Oldowan pebble tool technology. The earliest evidence for the use of the more advanced Acheulean technology are 900,000-year-old flint hand axes found in Spain. Notable human fossils from this most ancient period of European prehistory are Dmanisi in Georgia 1.8 mya, Lézignan-la-Cèbe 1.6 mya, Kozarnika in Bulgaria 1.4 mya, Atapuerca in Spain 1.2 mya, Mauer 1 from Germany 600k, Eartham Pit, Boxgrove England 478k, Swanscombe Man from England 400k, and Tautavel Man from France 400k.
The oldest complete hunting weapons ever found anywhere in the world were discovered in a coal mine in Schoningen, Germany in 1995 where three 380,000-year-old wooden javelins 6-7.5 feet long were unearthed.[6]
Middle Paleolithic
Eventually these European Homo erectus evolved through a series of intermediate speciations including Homo antecessor and Homo heidelbergensis into the species Homo neanderthalensis (since c. 200,000 BP) associated with Mousterian technologies. Our ancestors Homo sapiens also participated in this tool-making technique for a long time and they may have first settled Europe while this Mid-Paleolithic technique was still in use, though the issue is still unclear.
Ancient Upper Paleolithic
The bearers of most or all Upper Paleolithic technologies were H. sapiens. The oldest remains of modern humans from 43-45,000 years ago have been discovered in Italy[7] and in Britain.[8] Some locally developed transitional cultures (Szeletian and Lincombian-Ranisian-Jerzmanowician (LRJ) in Central Europe, Chatelperronian at the West and Uluzzian in the Southeast) use clearly Upper Paleolithic technologies at very early dates and there are doubts about who their carriers were: H. sapiens or Neanderthal man.
Nevertheless, the definitive advance of these technologies was made by the Aurignacian culture. By 37,000 BP, the Aurignacian culture and its technology had extended through most of Europe. The last Neanderthals seem to have been forced to retreat during this process to the southern half of the Iberian Peninsula.
The first but scarce works of art appear during this phase.
Middle Upper Paleolithic
Around 32,000 years ago, the Gravettian culture appeared in the Crimean Mountains (southern Ukraine).[9][10] By 24,000 BP the Solutrean and Gravettian cultures were present in the southwestern region of Europe. The Gravettian technology/culture has been theorized to have come with migrations of people from the Middle East, Anatolia, and the Balkans. They might be linked with the transitional cultures mentioned before, because their techniques have some similarities and are both very different from Aurignacian ones but this issue is very obscure. The Gravettian also appeared in the Caucasus and Zagros mountains. It soon disappeared from southwestern Europe, with the notable exception of the Mediterranean coasts of Iberia.
The Solutrean culture, extended from northern Spain to south-east France, includes not only a beautiful stone technology but also the first significant development of cave painting, the use of the needle and possibly that of the bow and arrow. The more widespread Gravettian culture is no less advanced, at least in artistic terms: sculpture (mainly venuses) is the most outstanding form of creative expression of these peoples.
Late Upper Paleolithic
Around 19,000 BP, Europe witnesses the appearance of a new culture, known as Magdalenian, possibly rooted in the old Aurignacian one. This culture soon supersedes the Solutrean area and also the Gravettian of Central Europe. However, in Mediterranean Iberia, Italy, the Balkans and Turkey, epi-Gravettian cultures continue evolving locally.
With the Magdalenian culture, Paleolithic development in Europe reaches its peak and this is reflected in art, owing to previous traditions of paintings and sculpture.
Epi-Paleolithic
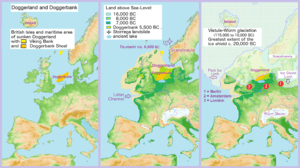
Around 12,500 BP, the Würm Glacial age ends. Slowly, through the following millennia, temperatures and sea levels rise, changing the environment of prehistoric people. During this time, Ireland and Great Britain become islands, and Scandinavia is separated from the main part of the European Peninsula. (They had all formerly been connected by a now-submerged region of the continental shelf known as Doggerland.) Nevertheless, Magdalenian culture persists until circa 10,000 BP, when it quickly evolves into two microlithist cultures: Azilian, in Spain and southern France, and Sauveterrian, in northern France and Central Europe. Though there are some differences, both cultures share several traits: the creation of very small stone tools called microliths and the scarcity of figurative art, which seems to have vanished almost completely, being replaced by abstract decoration of tools.[11]
In the late phase of this epi-Paleolithic period, the Sauveterrean culture evolves into the so-called Tardenoisian and influences strongly its southern neighbour, clearly replacing it in Mediterranean Spain and Portugal. The recession of the glaciers allows human colonization in Northern Europe for the first time. The Maglemosian culture, derived from the Sauveterre-Tardenois culture but with a strong personality, colonizes Denmark and the nearby regions, including parts of Britain.
Mesolithic
This was a transition period in the development of human technology between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term is mainly applied to the western part of Europe. The period began around 11,500 years ago and ended with the introduction of farming, the date of which varied in each geographical region. In some areas, such as the Near East, farming was already in use by the end of the Pleistocene. In areas with limited glacial impact the term "Epipaleolithic" is sometimes preferred for the period. Regions that experienced greater environmental effects as the last glacial period ended have a much more apparent Mesolithic era, lasting millennia. In northern Europe societies were able to live well on rich food supplies from the marshlands created by the warmer climate. Such conditions produced distinctive human behaviours that are preserved in the material record, such as the Maglemosian and Azilian cultures. Such conditions delayed the coming of the Neolithic to as late as 6000 BP in northern Europe.
As what Vere Gordon Childe termed the "Neolithic Package" (including agriculture, herding, polished stone axes, timber long houses and pottery) spread into Europe, the Mesolithic way of life was marginalised and eventually disappeared.[12] Controversy over the means of that dispersal is discussed below in the Neolithic section. Note that a "Ceramic Mesolithic" can be distinguished between 7200-5850 BP that ranged from southern to northern Europe.
Neolithic

The European Neolithic is believed to have arrived from the Near East, via Asia Minor, the Mediterranean waterway and also through the Caucasus. There has been a long discussion between migrationists (who claim that the Near Eastern farmers almost totally displaced the European native hunter-gatherers) and diffusionists (who claim that the process was slow enough to have occurred mostly through cultural transmission). A relationship has been suggested between the spread of agriculture and the diffusion of Indo-European languages, with several models of migrations trying to establish a relationship, like the Anatolian hypothesis, which sets the origin of Indo-European agricultural terminology in Anatolia.[13]
Prehistoric Neolithic
Apparently related with the Anatolian culture of Hacilar, the Greek region of Thessalia is the first place in Europe known to have acquired agriculture, cattle-herding and pottery. These early stages are known as pre-Sesklo culture. The Thessalian Neolithic culture soon evolves in the more coherent culture of Sesklo (c. 8000 BP), which is the origin of the main branches of Neolithic expansion in Europe. Practically all the Balkan Peninsula is colonized in the 6th millennium from there. That expansion, reaching the easternmost Tardenoisian outposts of the upper Tisza gives birth to the proto-Linear Pottery culture, a significant modification of the Balkan Neolithic that will be in the origin of one of the most important branches of European Neolithic: the Danubian group of cultures. In parallel, the coasts of the Adriatic and southern Italy witness the expansion of another Neolithic current of less clear origins. Settling initially in Dalmatia, the bearers of the Cardium Pottery culture may have come from Thessalia (some of the pre-Sesklo settlements show related traits) or even from Lebanon (Byblos). They are sailors, fishermen and sheep and goat herders, and the archaeological findings show that they mixed with natives in most places. Other early Neolithic cultures can be found in Ukraine and Southern Russia, where the epi-Gravettian locals assimilated cultural influxes from beyond the Caucasus (culture of Dniepr-Don and related) and in Andalusia (Spain), where the rare Neolithic of La Almagra Pottery appears without known origins very early (c. 7800 BP).
Middle Neolithic

This phase, starting 7000 years ago is marked by the consolidation of the Neolithic expansion towards western and northern Europe, but also by the (eruption)irruption of a new culture that, probably through violence, occupies most of the Balkans, substituting or rather subjugating the first Neolithic settlers. This is the culture of Dimini (Thessalia) and the related ones of Vinca-Turdas (Serbia and Romania) and Karanovo III-Veselinovo (Bulgaria and nearby areas), this last one more hybrid than the other two. Meanwhile, the tiny proto-Linear Pottery culture has given birth to two very dynamic branches: the Western and Eastern Linear Pottery Cultures. The latter is basically an extension of the Balkan Neolithic, but the more original western branch expands quickly, assimilating what today is Germany, the Czech Republic, Poland and even large parts of western Ukraine, historical Moldavia, the lowlands of Romania, and regions of France, Belgium and the Netherlands. This was all achieved in less than one thousand years. With expansion comes diversification and a number of local Danubian cultures start forming at the end of the 5th millennium. In the Mediterranean, the Cardium Pottery fishermen show no less dynamism and colonize/assimilate all of Italy and the Mediterranean regions of France and Spain. Even in the Atlantic, some groups among the native hunter-gatherers start slowly incorporating the new technologies. Among those, the most noticeable regions seem to be the southwest of Iberia, influenced by the Mediterranean but specially by the Andalusian Neolithic, which soon develops the first Megalithic burials (dolmens) and the area around Denmark (culture of Ertebölle), influenced by the Danubian complex.
Late Neolithic

This period occupies the first half of the 6th millennium BP and is rather quiet. The tendencies of the previous period consolidate, so we have a fully formed Neolithic Europe with five main cultural regions:
- Danubian cultures: from northern France to Western Ukraine. Now split into several local cultures, the most relevant ones being: the Romanian branch (culture of Boian) that expands into Bulgaria, the culture of Rössen that is preeminent in the west, and the culture of Lengyel of Austria and western Hungary, which will have a major role in the upcoming periods.
- Mediterranean cultures: from the Adriatic to eastern Spain, including Italy and large portions of France and Switzerland. These are also diversified into several groups.
- The area of Dimini-Vinca: Thessalia, Macedonia and Serbia, but extending its influence also to parts of the mid-Danubian basin (Tisza, Slavonia) and southern Italy.
- Eastern Europe: basically central and eastern Ukraine and parts of southern Russia and Belarus (culture of Dniepr-Don). Apparently these people were the ones who first domesticated horses (though some Paleolithic evidence could disprove it).
- Atlantic Europe: a mosaic of local cultures, some of them still pre-Neolithic, from Portugal to southern Sweden. Since around 5800 BP the western regions of France incorporate also the Megalithic style of burial.
There were also a few independent areas, including Andalusia, southern Greece and the western coasts of the Black Sea (culture of Hamangia).
Chalcolithic

Also known as Copper Age, European Chalcolithic is a time of changes and confusion. The most relevant fact is the infiltration and invasion of large parts of the territory by people originating from Central Asia, considered by mainstream scholars to be the original Indo-Europeans, although there are again several theories in dispute. Other phenomena are the expansion of Megalithism and the appearance of the first significant economic stratification and, related to this, the first known monarchies in the Balkan region.
The economy of the Chalcolithic, even in the regions where copper is not used yet, is no longer that of peasant communities and tribes: now some materials are produced in specific locations and distributed to wide regions. Mining of metal and stone is particularly developed in some areas, along with the processing of those materials into valuable goods.
- Ancient Chalcolithic
From c. 5500 to 5000 BP copper starts to be used in the Balkans, and Eastern and Central Europe. However, the key factor could be the use of horses, which would increase mobility. From c. 5500 onwards, Eastern Europe is apparently infiltrated by people originating from beyond the Volga (Yamna culture), creating a plural complex known as Sredny Stog culture, that substitutes the previous Dnieper-Donets culture, pushing the natives to migrate in a NW direction to the Baltic and Denmark, where they mix with natives (TRBK A and C). This may be correlated with the linguistic fact of the spread of Indo-European languages; see Kurgan hypothesis. Near the end of the period, another branch will leave many traces in the lower Danube area (culture of Cernavodă I), in what seems to be another invasion.
Meanwhile, the Danubian Lengyel culture absorbs its northern neighbours of the Czech Republic and Poland for some centuries, only to recede in the second half of the period. In Bulgaria and Wallachia (Southern Romania), the culture of Boian-Marica evolves into a monarchy with a clearly royal cemetery near the coast of the Black Sea. This model seems to have been copied later in the Tiszan region with the culture of Bodrogkeresztur. Labour specialization, economic stratification and possibly the risk of invasion may have been the reasons behind this development. The influx of early Troy (Troy I) is clear in both the expansion of metallurgy and social organization.
In the western Danubian region (the Rhine and Seine basins) the culture of Michelsberg displaces its predecessor, Rössen. Meanwhile, in the Mediterranean basin, several cultures (most notably Chassey in SE France and La Lagozza in northern Italy) converge into a functional union, of which the most significant characteristic is the distribution network of honey-coloured silex. Despite this unity, the signs of conflicts are clear, as many skeletons show violent injuries. This is the time and area where Ötzi, the famous man found in the Alps, lived. Another significant development of this period is that the Megalithic phenomenon starts spreading to most places of the Atlantic region, bringing agriculture with it to some underdeveloped regions there.
- Middle Chalcolithic
This period extends along the first half of the 3rd millennium BC. Most significant is the reorganization of the Danubians in the powerful Baden culture, that extends more or less to what would be the Austro-Hungarian empire in recent times. The rest of the Balkans is profoundly restructured after the invasions of the previous period but, with the exception of the culture of Coțofeni in a mountainous region, none of them show any eastern (or presumably Indo-European) traits. The new Ezero culture, in Bulgaria, shows the first traits of pseudo-bronze (an alloy of copper with arsenic). So does the first significant Aegean group: the Cycladic culture after 2800 BC.
In the North, for some time the supposedly Indo-European groups seem to recede temporarily, suffering a strong cultural Danubianization. In the East, the peoples of beyond the Volga (Yamna culture), surely eastern Indo-Europeans, ancestors of the Iranian Scythians, take over southern Russia and Ukraine. In the Western world the only sign of unity comes from the Megalithic super-culture, which extends now from southern Sweden to southern Spain, including large parts of southern Germany as well. But the Mediterranean and Danubian groupings of the previous period appear fragmented into many smaller pieces, some of them apparently backward in technological matters. From c. 2800 BC, the Danubian Seine-Oise-Marne culture pushes directly or indirectly southwards, destroying most of the rich Megalithic culture of western France. After c. 2600 BC, several phenomena will prefigure the changes of the upcoming period:
Large towns with stone walls appear in two different areas of the Iberian Peninsula: one in the Portuguese region of Estremadura (culture of Vila Nova de Sao Pedro), strongly embedded in the Atlantic Megalithic culture; the other near Almería (SE Spain), centred around the large town of Los Millares, of Mediterranean character, probably affected by eastern cultural influxes (tholoi). Despite the many differences the two civilizations seem to be in friendly contact and to have productive exchanges. In the area of Dordogne (Aquitaine, France), a new unexpected culture of bowmen appears: it is the culture of Artenac, that soon takes control of western and even northern France and Belgium. In Poland and nearby regions, the putative Indo-Europeans reorganize and consolidate again with the culture of the Globular Amphoras. Nevertheless, the influence of many centuries in direct contact with the still-powerful Danubian peoples has greatly modified their culture.
- Late Chalcolithic
This period extends from c. 2500 BC to c. 1800 or 1700 BC (depending on the region). The dates are general for the whole of Europe, and the Aegean area is already fully in the Bronze Age. ca. 2500 BC the new Catacomb culture (proto-Cimmerians?), whose origins are obscure but who are also Indo-Europeans, displaces the Yamna peoples in the regions north and east of the Black Sea, confining them to their original area east of the Volga. The Catacomb culture is the first to introduce corded pottery decorations into the steppes and shows a profuse use of the polished battle axe, providing a link to the West. Parallels with the Afanasevo culture, including provoked cranial deformations, provide a link to the East. Some of these infiltrate Poland and may have played a significant but unclear role in the transformation of the culture of the Globular Amphorae into the new Corded Ware culture.
Whatever happened, the fact is that c. 2400 BC this people of the Corded Ware replace their predecessors and expand to Danubian and Nordic areas of western Germany. One related branch invades Denmark and southern Sweden (Scandinavian culture of Individual Sepultures), while the mid-Danubian basin, though showing more continuity, shows also clear traits of new Indo-European elites (Vučedol culture). Simultaneously, in the west, the Artenac peoples reach Belgium. With the partial exception of Vučedol, the Danubian cultures, so buoyant just a few centuries ago, are wiped off the map of Europe. The rest of the period is the story of a mysterious phenomenon: the Beaker people. This group seems to be of mercantile character and to like being buried according to a very specific, almost invariable, ritual. Nevertheless, out of their original area of western Central Europe, they appear only inside local cultures, so they never invaded and assimilated but rather went to live among those peoples, keeping their way of life. This is why they are believed to be merchants.
The rest of the continent remains mostly unchanged and in apparent peace. From c. 2300 BC the first Beaker Pottery appears in Bohemia and expands in many directions but particularly westward, along the Rhone and the sea shores, reaching the culture of Vila Nova (Portugal) and Catalonia (Spain) as their limits. Simultaneously but unrelatedly, c. 2200 BC in the Aegean region, the Cycladic culture decays, being substituted by the new palatine phase of the Minoan culture of Crete.
The second phase of Beaker Pottery, from c. 2100 BC onwards, is marked by the displacement of the centre of this phenomenon to Portugal, inside the culture of Vila Nova. This new centre's influence reaches to all southern and western France but is absent in southern and western Iberia, with the notable exception of Los Millares. After c. 1900 BC, the centre of the Beaker Pottery returns to Bohemia, while in Iberia we see a decentralization of the phenomenon, with centres in Portugal but also in Los Millares and Ciempozuelos.
Bronze Age
Though the use of bronze started much earlier in the Aegean area, it is not before 1800 BC that it reaches southern Spain, while Central Europe will wait another century (c. 1700 BC) and the Atlantic region would remain Chalcolithic until 1300 BC. In any case, the date of 1800/1700 BC can be considered typical for the start of this stage in Europe in general, although some scholars claim earlier dates for the introduction of bronze (this may be caused by the slim barrier between copper and bronze, an alloy of the former).
- c. 1800 BC, the culture of Los Millares in SW Spain is substituted by that of El Argar, fully of the Bronze Age, which may well have been a centralized state.
- c. 1700 BC, the Central European cultures of Unetice, Adlerberg, Straubing and pre-Lausitz start working the Bronze, a technique that reached them through the Balkans and Danube.
- c. 1600 BC is considered a good approximate date to place the start of Mycenaean Greece, after centuries of infiltration of Indo-European Greeks from an unknown origin.
- c. 1500 BC, most of these Central European cultures are unified in the powerful Tumulus culture. Simultaneously but unrelatedly, the culture of El Argar starts its phase B, characterized by a detectable Aegean influence (pithoi burials). About this time, it is believed that Minoan Crete fell under the rule of the Mycenaean Greeks.
- c. 1300 BC, the Indo-European cultures of Central Europe (among them Celts, Italics and certainly Illyrians) change the cultural phase conforming to the expansionist Urnfield culture, starting a quick expansion that brings them to occupy most of the Balkans, Asia Minor, where they destroy the Hittite Empire (conquering the secret of iron smelting), NE Italy, parts of France, Belgium, the Nederlands, NE Spain and SW England.
Derivations of this sudden expansion are the Sea Peoples that attacked Egypt unsuccessfully for some time, including the Philistines (Pelasgians?) and the Dorians, most likely hellenized members of this group that ended invading Greek itself and destroying the might of Mycene and, later, Troy.
Simultaneously, around this date, the culture of Vila Nova de Sao Pedro (that lasted 13 centuries in its urban form) vanishes into a less spectacular one but finally with bronze. The centre of gravity of the Atlantic cultures (Atlantic Bronze complex) is now displaced towards Great Britain. Also about this date, the culture of Villanova, possible precursor of the Etruscan civilization, appears in central Italy (possibly with an Aegean origin).
Iron Age
Though the use of iron was known to the Aegean peoples about 1100 BC, it didn't reach Central Europe before 800 BC, giving way to the Hallstatt culture, an Iron Age evolution of the Urnfield culture.
Around that time the Phoenicians, benefitting from the disappearance of the Greek maritime power (Greek Dark Ages) founded their first colony at the entrance of the Atlantic Ocean: in Gadir (modern Cádiz), most likely as a merchant outpost to convey the many mineral resources of the Iberian Peninsula and the British Isles.
Nevertheless, from the 7th century BC onwards, the Greek nation recovers its power and starts its own colonial expansion, founding Massalia (modern Marseilles) and its Iberian outpost of Emporion (modern Empúries). This last thing wasn't done before the Iberians could reconquer Catalonia and the Ebro valley from the Celts, separating physically the Iberian Celts from their continental neighbours.
The second phase of the European Iron Age is defined particularly by the Celtic La Tène culture, that starts near 400 BC, followed by a large expansion of this people into the Balkans, the British Isles (where they assimilated druidism) and other regions of France and Italy.
The decline of Celtic power under the expansive pressure of Germanic tribes (originally from Scandinavia and Lower Germany) and the forming Roman Empire, in the last century BC, is also that of the end of prehistory properly speaking; though many regions of Europe remained yet illiterate and therefore out of written history for many centuries yet, we must place the boundary somewhere and this date, near the start of our calendar, seems quite convenient. The remaining is regional prehistory (or in most cases protohistory) but no longer European prehistory as a whole.
Genetic history
The genetic history of Europe has been inferred by observing the patterns of genetic diversity across the continent and in the surrounding areas. Use has been made of both classical genetics and molecular genetics.[14][15] Analysis of the DNA of the modern population of Europe has mainly been used but use has also been made of ancient DNA.
This analysis has shown that modern man entered Europe from the Near East before the Last Glacial Maximum but retreated to refuges in southern Europe in this cold period. Subsequently people spread out over the whole continent, with subsequent limited immigration from the Near East and Asia.[16]
Linguistic history
What languages were spoken in Europe during the prehistorical period is controversial. It is generally assumed that non-Indo-European languages were spoken in Western and Central Europe prior to the introduction of Proto-Indo-European in the Bronze Age (the majority Kurgan hypothesis locates Proto-Indo-European in Eastern Europe, thus clearly within Europe). A Vasconic substratum hypothesis for Western Europe, with influence from a "Semitidic" language, has been postulated but roundly rejected.[17] Kalevi Wiik has suggested that Finno-Ugric languages may have been spoken across the whole of northern Europe at the end of the Last Glacial Maximum.[18] That hypothesis has been rejected by mainstream linguistics.
A tiny minority of scholars have argued for a deeper time depth of Proto-Indo-European in Europe. A group of scholars, led by Mario Alinei, considers that Indo-European has been spoken in Europe since the Last Glacial Maximum, in the Paleolithic Continuity Theory. Jonathan Adams and Marcel Otte have a slightly different point of view in suggesting that Indo-European spread immediately after the Younger Dryas.[19]
Proto-Indo-European is believed to have given rise to most European languages in the historical period. However, it is known that a number of non-Indo-European languages were spoken in the proto-historical part of prehistoric Europe. Northeastern Europe has Uralic languages, which have been spoken in the region since prehistoric times.
Donald Ringe rejects all the aforementioned specific proposals on grounds of the findings of language geography in areas with "tribal", pre-state societies, such as North America prior to European colonization, which renders a Neolithic Europe dominated by only a few language families extremely implausible, even impossible. He argues that prior to the spread of the Indo-European and Uralic families, Europe must have been a place of great linguistic diversity.[20]
See also
- Archaeological sites sorted by continent and age
- Atlantic Europe
- European megalithic culture
- Mediterranean Europe
- Prehistoric Britain
- Prehistoric Cyprus
- Prehistoric France
- Prehistoric Georgia
- Prehistoric Hungary
- Prehistoric Iberia
- Prehistoric Ireland
- Prehistoric Romania
- Prehistoric Transylvania
- Prehistoric Scotland
- Prehistory of Brittany
- Prehistory of Poland (until 966)
- Synoptic table of the principal old world prehistoric cultures
Notes
- ↑ "Fossils Reveal Clues on Human Ancestor". The New York Times. 20 September 2007.
- ↑ http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-28693371
- ↑ "Fossil Teeth Put Humans in Europe Earlier Than Thought". The New York Times. 2 November 2011.
- ↑ http://www.nytimes.com/2015/06/16/science/dna-deciphers-roots-of-modern-europeans.html?_r=0
- ↑ http://www.ucl.ac.uk/archaeology/calendar/articles/20100924
- ↑ http://archive.archaeology.org/9705/newsbriefs/spears.html
- ↑ Benazzi, S.; Douka, K.; Fornai, C.; Bauer, C. C.; Kullmer, O.; Svoboda, J. Í.; Pap, I.; Mallegni, F.; Bayle, P.; Coquerelle, M.; Condemi, S.; Ronchitelli, A.; Harvati, K.; Weber, G. W. (2011). "Early dispersal of modern humans in Europe and implications for Neanderthal behaviour". Nature. 479 (7374): 525–8. doi:10.1038/nature10617. PMID 22048311.
- ↑ Higham, T.; Compton, T.; Stringer, C.; Jacobi, R.; Shapiro, B.; Trinkaus, E.; Chandler, B.; Gröning, F.; Collins, C.; Hillson, S.; o’Higgins, P.; Fitzgerald, C.; Fagan, M. (2011). "The earliest evidence for anatomically modern humans in northwestern Europe". Nature. 479 (7374): 521–4. doi:10.1038/nature10484. PMID 22048314.
- ↑ Prat, Sandrine; Péan, Stéphane C.; Crépin, Laurent; Drucker, Dorothée G.; Puaud, Simon J.; Valladas, Hélène; Lázničková-Galetová, Martina; van der Plicht, Johannes; Yanevich, Alexander (17 June 2011). "The Oldest Anatomically Modern Humans from Far Southeast Europe: Direct Dating, Culture and Behavior". plosone. Retrieved 21 June 2011.
- ↑ Carpenter, Jennifer (20 June 2011). "Early human fossils unearthed in Ukraine". BBC. Retrieved 21 June 2011.
- ↑ http://www.beloit.edu/~museum/logan/paleoexhibit/masdazil.htm#thumbnails
- ↑ Childe 1925
- ↑ The supposed autochthony of Hittites, the Indo-Hittite hypothesis and migration of agricultural "Indo-European" societies became intrinsically linked together by C. Renfrew 2001
- ↑ Cavalli-Sforza et al. 1994
- ↑ Metspalu et al. 2004
- ↑ Achilli et al. 2004
- ↑ Vennemann 2003
- ↑ Wiik 2002.
- ↑ Adams and Otte 1999
- ↑ Ringe, Don (January 6, 2009). "The Linguistic Diversity of Aboriginal Europe". Language Log. Mark Liberman. Retrieved 22 September 2011.
References
- Achilli, Alessandro; Rengo, Chaira; Magri, Chiara; Battaglia, Vincenza; Olivieri, Anna; Scozari, Rosaria; Cruciani, Fulvio; Zeviani, Massimo; Briem, Egill; Carelli, Valerio; Moral, Pedro; Dugoujon, Jean-Michel; Roostalu, Urmas; Loogväli, Eva-Liss; Kivisild, Toomas; Bandelt, Hans-Jürgen; Richards, Martin; Villems, Richard; Santachiara-Benerecetti, A. Silvana; Semino, Ornella; Torroni, Antonio (2004). "The Molecular Dissection of mtDNA Haplogroup H Confirms that the Franco-Cantabrian Glacial Refuge was a Major Source for the European Gene Pool". American Journal of Human Genetics. 75: 910–918. doi:10.1086/425590. PMC 1182122
 . PMID 15382008.
. PMID 15382008. - Adams, Jonathan; Otte, Marcel (1999). "Did Indo-European Languages Spread Before Farming?". Current Anthropology. 40 (1): 73–77. doi:10.1086/515804.
- Childe, V. Gordon. 1925. The Dawn of European Civilization. New York: Knopf.
- Childe V.Gordon. 1950. Prehistoric Migrations in Europe. Olso: Aschehoug.
- Cavalli-Sforza L.L., Paolo Menozzi, Alberto Piazza. 1994. The History and Geography of Human Genes. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Finnilä, Saara; Lehtonen, Mervi S.; Majamaa, Kari (2001). "Phylogenetic Network for European mtDNA". American Journal of Human Genetics. 68: 1475–1484. doi:10.1086/320591. PMC 1226134
 . PMID 11349229.
. PMID 11349229. - Gimbutas, M (1980). "The Kurgan wave migration (c. 3400–3200 B.C.) into Europe and the following transformation of culture". Journal of Near Eastern Studies. 8: 273–315.
- Macaulay, Vincent; Richards, Martin; Hickey, Eileen; Vega, Emilce; Cruciani, Fulvio; Guida, Valentina; Scozzari, Rosaria; Bonné-Tamir, Batsheva; Sykes, Bryan; Torroni, Antonio (1999). "The Emerging Tree of West Eurasian mtDNAs: A Synthesis of Control-Region Sequences and RFLPs". American Journal of Human Genetics. 64: 232–249. doi:10.1086/302204. PMC 1377722
 . PMID 9915963.
. PMID 9915963. - Metspalu, Mait, Toomas Kivisild, Ene Metspalu, Jüri Parik, Georgi Hudjashov, Katrin Kaldma, Piia Serk, Monika Karmin, Doron M Behar, M Thomas P Gilbert, Phillip Endicott, Sarabjit Mastana, Surinder S Papiha, Karl Skorecki, Antonio Torroni and Richard Villems. 2004. "Most of the extant mtDNA boundaries in South and Southwest Asia were likely shaped during the initial settlement of Eurasia by anatomically modern humans." BMC Genetics 5
- Piccolo, Salvatore. 2013. Ancient Stones: The Prehistoric Dolmens of Sicily. Abingdon (GB): Brazen Head Publishing.
- Renfrew, Colin. 2001. "The Anatolian origins of Proto-Indo-European and the autochthony of the Hittites." In Greater Anatolia and the Indo-Hittite Language Family, R. Drews ed., pp. 36–63. Washington, DC: Institute for the Study of Man.
- Venemann, Theo. 2003. Europa Vasconica, Europa Semitica. Trends in Linguistic Studies and Monographs No. 138. New York and Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
- Wiik, Kalevi. 2002. Europpalaisten Juuret. Athens: Juvaskylä
External links
| Wikivoyage has travel information for Prehistoric Europe. |
- Neolithic and Chalcolithic Artifacts from the Balkans
- Central European Neolithic Chronology
- South East Europe pre-history summary to 700BC
- Prehistoric art of the Pyrenees
Paleolithic sanctuaries:
