T-box
For the computer science term, see Tbox.
| T-box | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
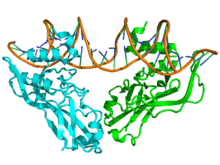 Crystallographic structure of the TBX3 protein dimer (cyan and green) complexed with DNA (brown) based on the PDB: 1h6f coordinates. | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | T-box | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00907 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001699 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PS50252 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1xbr | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1xbr | ||||||||
| |||||||||
T-box refers to a group of transcription factors involved in limb and heart development.[1]
In humans and some other animals, defects in the TBX5 gene expression can lead to finger-like thumbs and ventricular septal defects in which there is no separation between the left and right ventricle of the heart and are responsible for Holt-Oram syndrome.
TBX3 is associated with ulnar-mammary syndrome in humans, but is also responsible for the presence or absence of dun color in horses, and has no deleterious effects whether expressed or not.[2]
Genes encoding T-box proteins include:
See also
References
- ↑ Wilson V, Conlon FL (2002). "The T-box family". Genome Biol. 3 (6): REVIEWS3008. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-6-reviews3008. PMC 139375
 . PMID 12093383.
. PMID 12093383. - ↑ "A Horse of a Different Color: Genetics of camouflage and the dun pattern". Science Daily. December 21, 2015. Retrieved June 25, 2016.
Further reading
- Meisler (1997). "Mutation watch: Mouse brachyury (T), the T-box gene family, and human disease." (PDF).
External links
- T-Box Domain Proteins at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.